File:Inverse contour example.png
From Applied Optics Wiki
Revision as of 23:34, 21 January 2024 by Finlay Nelson (talk | contribs) (The combination of n and k (real and imaginary components of refractive index) that result in scattering and absorption values that match those generated by the forward Mie model for a charged nanosphere of equal size. The overlap of these contours is...)
Inverse_contour_example.png (395 × 280 pixels, file size: 17 KB, MIME type: image/png)
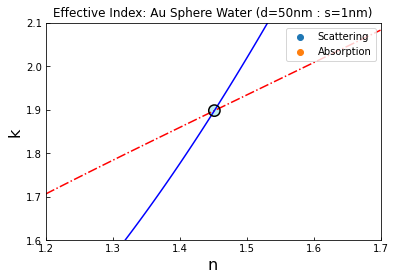
The combination of n and k (real and imaginary components of refractive index) that result in scattering and absorption values that match those generated by the forward Mie model for a charged nanosphere of equal size. The overlap of these contours is the solution to the effective refractive index problem. This particular example is specific to a 50nm diameter Au sphere in water with a 1nm shell thickness emulating the charge-dependent effects of a -300mV applied potential when illuminated with a wavelength of 400nm.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 23:34, 21 January 2024 |  | 395 × 280 (17 KB) | Finlay Nelson (talk | contribs) | The combination of n and k (real and imaginary components of refractive index) that result in scattering and absorption values that match those generated by the forward Mie model for a charged nanosphere of equal size. The overlap of these contours is... |
- You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page links to this file: